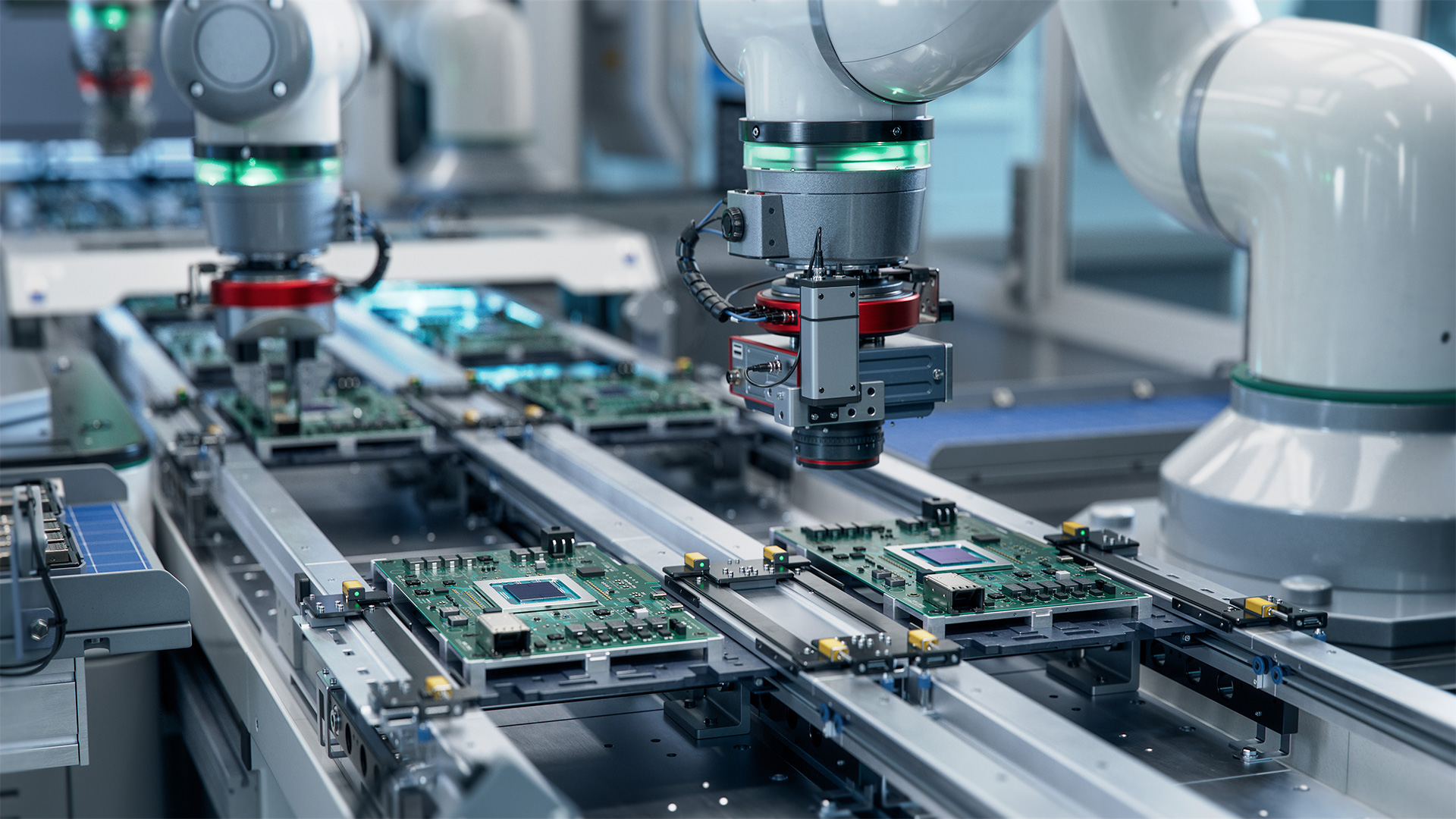
Smart factories, also known as factories of the future, are factories that rely on advanced technologies such as robotization, data integration and the Internet of Things (IoT) to automate processes and create a connected data-driven ecosystem. Companies that implement these solutions gain a significant advantage in improving their processes and competitiveness.
The importance of smart factories as factors of competitiveness
For manufacturers seeking to maintain and enhance their competitiveness, the transition to smart factories is a strategic imperative. In a volatile and demanding global market, smart factories offer a significant advantage by providing unparalleled efficiency and flexibility.
The integration of advanced technologies allows for real-time monitoring of production lines, leading to a proactive approach to maintenance and quality control. Data-driven insights generated within smart factories empower manufacturers to optimize their entire value chain, from raw materials sourcing to final delivery.
Smart factories benefit from enhanced visibility and control over the production processes, facilitating adaptation to market changes and fluctuating demand.
Automating repetitive or highly complex tasks enables manufacturers to allocate human resources to activities such as research and development, accelerating their capacity for innovation.
Core pillars of smart factory transformation
Automation and robotization
Automation and robotization are fundamental to the smart factory, transforming traditional manufacturing into a more precise and efficient process. These technologies include sophisticated systems that perform complex and repetitive tasks with a high degree of accuracy.
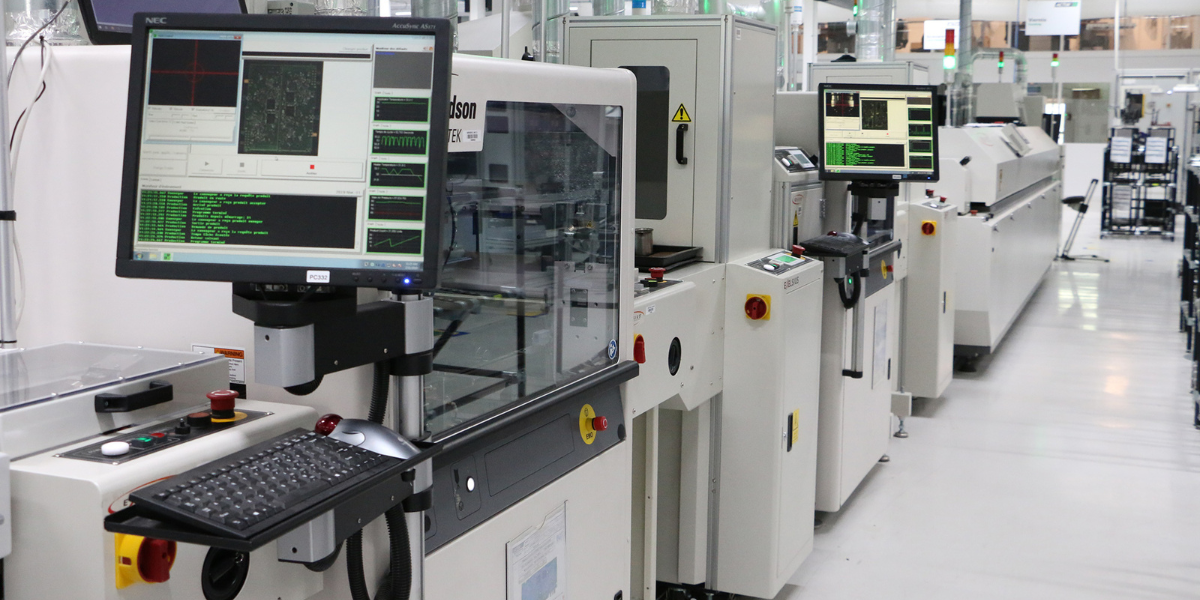
Robotics are used for high-precision applications such as component placement in Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and in the execution of Automated Optical Inspection (AOI). This accelerates production speed and significantly reduces the margin of error, resulting in superior quality products.
The advent of collaborative robots (cobots) allows for a more flexible production environment in which robots and human workers can safely operate side by side, augmenting human capabilities rather than replacing them. This synergy enables a dynamic allocation of tasks, with cobots handling monotonous, heavy or hazardous tasks, while human expertise is directed towards problem-solving, quality assurance and system oversight.
Data integration and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
The smart factory’s primary advantage is its ability to integrate data, a function primarily enabled by the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT).
This is a network consisting of interconnected sensors, devices and machines that continuously generate and transmit large amounts of data from every point in the production plant. This real-time data stream provides a complete overview of operations. IIoT allows to monitor precisely key parameters such as machine performance, component status and environmental conditions in real time.
Integrating and centralizing information from all sensors around the factory makes it possible to perform advanced analytics, providing a deeper understanding of process efficiencies and potential bottlenecks. For example data from ICT (In-Circuit Test) and FCT (Functional Circuit Test) stations can be aggregated to identify production failure trends, allowing for immediate corrective actions.
Advanced technologies for enhanced manufacturing
Artificial intelligence and machine learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning transform the smart factory from a connected environment into an intelligent, predictive one. These technologies process the vast data stream from the IIoT to derive actionable insights that surpass human analytical capabilities.
In quality control, AI-driven vision systems can detect microscopic defects in a Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) with a level of precision and speed that is impossible for the human eye to attain. This enables a nearly zero defect rate and prevents faulty products from moving further along in the production process.
Machine learning can be used for predictive maintenance by analyzing operational data from machines to forecast potential failures before they occur. This proactive approach enables for maintenance to be scheduled precisely when needed, eliminating unexpected downtime and extending the lifespan of critical equipment.
Smart factories allow for advanced decision-making to maximize output and efficiency by transforming raw data into a strategic asset to continuously improve the manufacturing process.
Digital twin and simulation
A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical process, product or entire factory floor, created using real-time data from IIoT sensors and other connected systems. This dynamic model allows engineers and designers to simulate various scenarios and test changes without disrupting the actual production line.
For example, a digital twin can be used to experiment with a new factory layout, optimize a design for manufacturing strategy or evaluate the effect of a process change on overall efficiency and productivity. The simulation provides a safe environment for exploring different variables and identifying potential issues before they become costly problems. This is particularly valuable in the Production Part Approval Process (PPAP), where new parts or processes can undergo thorough validation in a virtual environment.
Digital twins are strategic assets that help manufacturers accelerate innovation cycles and changes by enabling safe testing without disrupting factory processes prior to validation.
Cybersecurity and data integrity
The interconnected nature of smart factories also introduces significant cybersecurity risks. Securing the integrity and confidentiality of data is essential for ensuring operational continuity and protecting intellectual property.
A strong cybersecurity framework is essential to defend against threats that could compromise production lines, manipulate data or steal sensitive information, such as the bill of materials. This requires a multi-layered approach, including network segmentation to isolate critical data from standard IT networks and strong authentication protocols for all connected devices and systems. Continuous monitoring and threat detection are also vital to identify and respond to malicious activities in real time.
A strict cybersecurity policy is fundamental to ensure that all information used by the smart factory is reliable. Without such a policy, the entire ecosystem is vulnerable to disruption and piracy.
Implementing smart factory solutions
The successful implementation of smart factory solutions is a strategic, multi-phased long-term process rather than a single event. It requires a well-defined roadmap that begins with a thorough evaluation of existing processes and pain points.
Implementing smart factory solutions requires a step by step approach. For example, you may first deploy IIoT sensors on critical machinery to collect data for predictive maintenance before tackling more complex AI-driven optimization. This modular strategy minimizes disruption and allows for continuous adaptation.
Taking a strategic, incremental approach allows you to manage the transition smoothly, upskill your workforce, and establish a sustainable, successful smart factory ecosystem.
For a smooth transition: choose a dedicated partner
Implementing smart factory solutions requires an ambitious reorganization of your current processes. ACTIA is an Electronic Manufacturing Services (EMS) company dedicated to helping manufacturers transition to factories of the future for enhanced productivity, quality, and competitiveness.